Introduction AI in healthcare
AI in healthcare is revolutionizing how medicine is delivered by improving diagnostics, automating operations, and enhancing patient care. As of 2025, over 88 percent of healthcare providers globally report using at least one form of AI. Imagine a hospital that detects sepsis risk before symptoms appear or a model that identifies cancer cells faster than a trained specialist. These breakthroughs are not projections. They are real, in use, and reshaping care today. If you’re a clinician, policymaker, investor, or patient, understanding AI in healthcare is crucial to navigating what comes next.
Key Takeaways
- AI enhances diagnosis, triage, and workflow efficiency.
- Real-world deployments show reduced errors and better patient outcomes.
- Ethical risks and regulatory uncertainty must be addressed.
- Future innovations will focus on personalization, robotics, and global accessibility.
Also Read: Predictive diagnostics for early disease detection
Table of contents
What Is AI in Healthcare?
Artificial intelligence in healthcare refers to computer systems that mimic human cognition to improve clinical decision-making, automate tasks, and interpret complex medical data. AI applications include diagnostic imaging, personalized treatment planning, virtual assistants, robotic surgery, and administrative automation.
The global healthcare AI market was worth 16.3 billion dollars in 2022 and is expected to grow to 173.5 billion dollars by 2029, according to Fortune Business Insights. This rapid adoption reflects the demand for scalable, cost-efficient, and data-driven health services.
Also Read: Growing Uses of Artificial intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
Core Applications of AI in Healthcare
1. Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
AI models such as CheXNet detect pneumonia on chest X-rays with 92 percent accuracy, rivaling radiologists (Rajpurkar et al.). These tools can identify early signs of tumors, strokes, and fractures. In dermatology, Stanford’s convolutional neural network classifies skin cancer with 91 percent accuracy, matching expert-level performance (Esteva et al.).
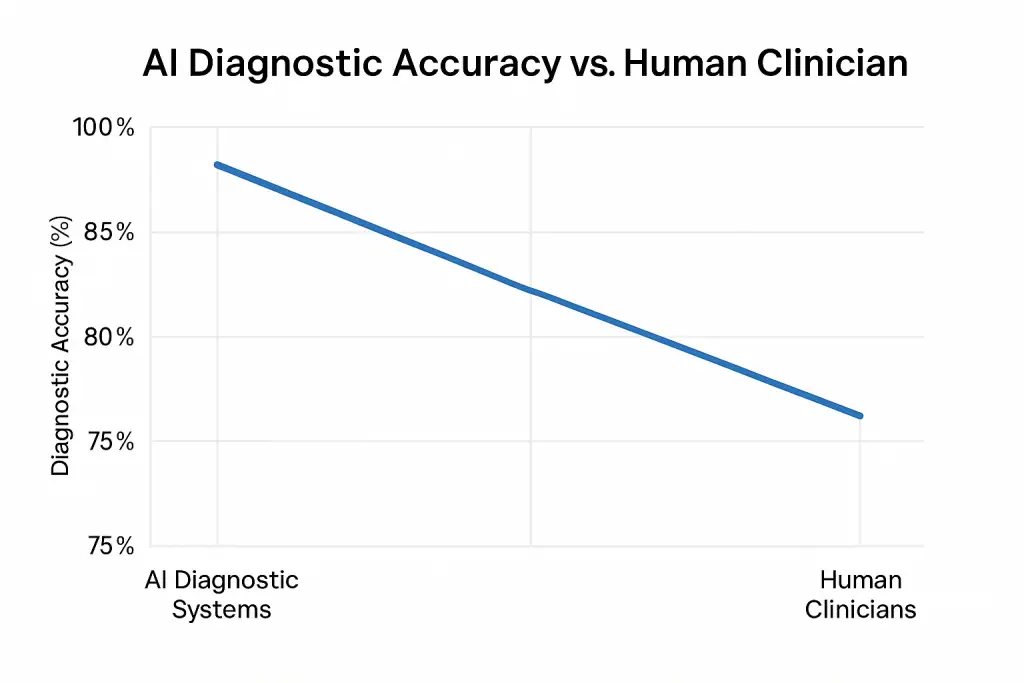
2. Predictive Analytics
AI systems analyze electronic health records to predict adverse events before they occur. Mount Sinai’s deep learning model forecasts heart failure risk 48 hours in advance. According to the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, AI-based alerts led to a 35 percent reduction in ICU transfers.
Predictive models also identify readmission risk, manage chronic diseases, and support emergency response planning.
3. Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
Over 100 million people use AI chatbots like Babylon Health, Ada Health, and Buoy to manage symptoms and receive care recommendations. In the UK, Babylon’s triage system reduced general practitioner workload by 15 percent.
Voice-based systems help elderly patients manage medication, track vitals, and connect with caregivers remotely.
4. Drug Discovery and Genomics
AI reduces early-stage drug discovery time by 40 to 60 percent, according to Deloitte. Atomwise’s neural networks screened 10 million compounds in 72 hours to identify antiviral candidates. Insilico Medicine’s platform generates drug targets and molecular structures using deep reinforcement learning.
In genomics, AI pinpoints gene-disease relationships and tailors treatment protocols to individual DNA profiles.
5. Robotic Surgery and Wearables
The da Vinci surgical system has completed more than 10 million procedures globally. AI improves precision, reduces recovery time, and limits surgical complications. In orthopedics, robots assist with joint alignment and reduce revision rates.
Wearables such as Fitbit and Apple Watch use AI to detect arrhythmias, monitor oxygen levels, and alert users to abnormal patterns. These tools support continuous remote monitoring and early intervention.
6. EHR and Administrative Automation
Clinicians spend up to 40 percent of their time on documentation. AI-powered tools like Nuance DAX transcribe clinical conversations into notes, saving an average of seven hours per week per physician. Other tools automate billing, coding, scheduling, and patient reminders.
Also Read: AI-driven healthcare innovations
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Early Diagnosis | Reduces mortality and improves treatment success. |
| Improved Workflow Efficiency | Saves time and reduces clinician burnout. |
| Cost Reduction | Avoids unnecessary procedures and readmissions. |
| Access to Care | Enables diagnostics in underserved or rural areas. |
| Personalization | Tailors treatment based on genetic and behavioral data. |
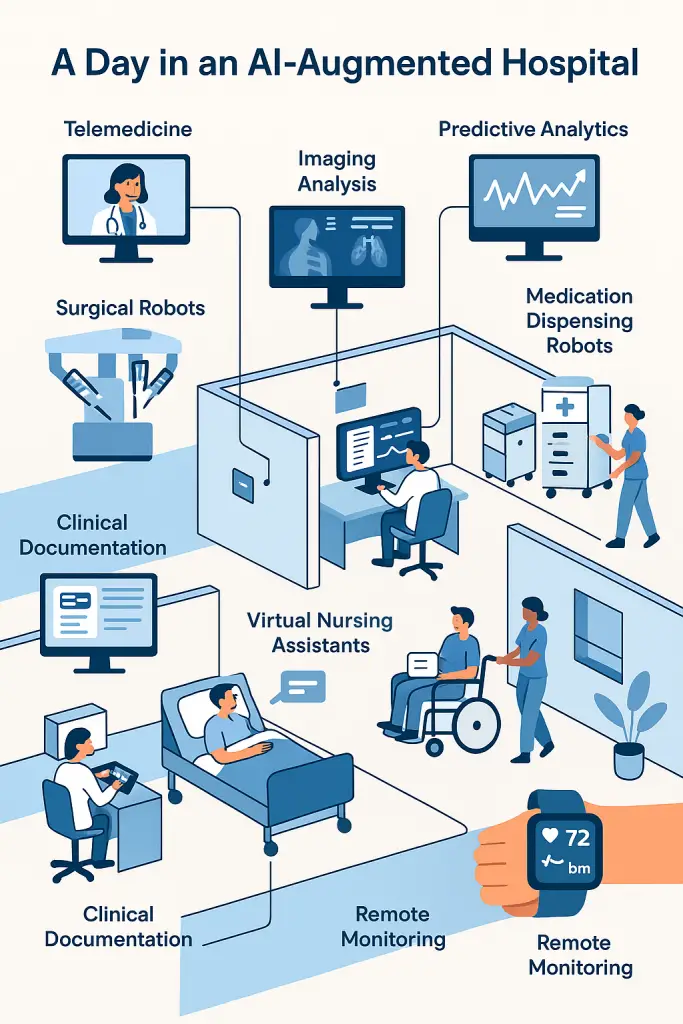
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
AI systems require access to sensitive patient data. Between 2020 and 2023, healthcare data breaches rose by 95 percent (IBM Security). Solutions include data encryption, secure cloud storage, and role-based access controls.
Algorithmic Bias
Stanford researchers found that some AI models underdiagnose heart failure in Black patients by 36 percent. Bias in training data can lead to unequal care. Fairness-aware algorithms, diverse datasets, and routine audits are needed.
Explainability
Many AI systems are black boxes, offering little insight into how they make decisions. This hinders trust. Explainable AI techniques like SHAP and LIME help clinicians understand feature contributions, improving model transparency.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Only 343 AI-based medical tools have been FDA-cleared as of 2024. Guidelines for continuously learning models remain inconsistent. Developers must work with regulators early and design models with auditability and compliance in mind.
Also Read: ChatGPT Beats Doctors in Disease Diagnosis

Real-World Case Studies
Cleveland Clinic – Stroke Risk
Cleveland Clinic uses AI to analyze speech and movement for early signs of stroke. Among high-risk patients, stroke-related mortality dropped by 13 percent after implementation.
DeepMind and Moorfields Eye Hospital
DeepMind developed an AI model that diagnoses over 50 retinal conditions with expert-level accuracy. This tool allows UK clinicians to prioritize patients who need urgent care.
Mayo Clinic – Heart Failure Screening
Mayo Clinic’s AI model detects asymptomatic heart failure from EKGs. Used across 15 sites, this system increased detection rates by 22 percent while maintaining a low false-positive rate.
Babylon Health – Virtual Consultations
Babylon’s app has conducted over 5 million consultations globally. In Rwanda, it enabled population-wide triage where access to physicians is limited.
Future Trends in AI Healthcare
Generative AI for Notes: Tools like Microsoft Copilot auto-generate medical records from voice conversations.
Multimodal Models: AI systems that analyze combined text, image, and lab data for more accurate decisions.
AI for Global Health: AI supports infectious disease tracking and maternal care in low-income countries.
AI Surgical Navigation: Real-time augmented reality systems for operating room guidance.
Personalized Digital Twins: AI simulations of individual patients used to test treatments virtually.
Responsible AI Adoption Framework
| Stage | Action |
|---|---|
| Problem Definition | Identify a clinical or operational gap. |
| Vendor Evaluation | Choose tools with published performance metrics and regulatory approval. |
| Pilot Testing | Launch small-scale tests and gather feedback. |
| Training and Onboarding | Educate staff on AI capabilities and limitations. |
| Monitoring and Feedback | Continuously evaluate AI performance and patient impact. |
| Governance | Assign accountability, update models regularly, and audit outcomes. |
Final Thoughts
AI in healthcare is moving from hype to impact. Hospitals and health systems are already seeing gains in diagnostics, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Yet real challenges remain ethical risks, trust gaps, and regulation. These need thoughtful leadership, inclusive design, and clear accountability. When done right, AI doesn’t just enhance medicine. It makes care more human.
References
Parker, Prof. Philip M., Ph.D. The 2025-2030 World Outlook for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. INSEAD, 3 Mar. 2024.
Khang, Alex, editor. AI-Driven Innovations in Digital Healthcare: Emerging Trends, Challenges, and Applications. IGI Global, 9 Feb. 2024.
Singla, Babita, et al., editors. Revolutionizing the Healthcare Sector with AI. IGI Global, 26 July 2024.
Topol, Eric J. Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again. Basic Books, 2019.
Nelson, John W., editor, et al. Using Predictive Analytics to Improve Healthcare Outcomes. 1st ed., Apress, 2021.
Subbhuraam, Vinithasree. Predictive Analytics in Healthcare, Volume 1: Transforming the Future of Medicine. 1st ed., Institute of Physics Publishing, 2021.
Kumar, Abhishek, et al., editors. Evolving Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: New AI Techniques for Real-Time Interventions. The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2022.
Tetteh, Hassan A. Smarter Healthcare with AI: Harnessing Military Medicine to Revolutionize Healthcare for Everyone, Everywhere. ForbesBooks, 12 Nov. 2024.
Lawry, Tom. AI in Health: A Leader’s Guide to Winning in the New Age of Intelligent Health Systems. 1st ed., HIMSS, 13 Feb. 2020.
Holley, Kerrie, and Manish Mathur. LLMs and Generative AI for Healthcare: The Next Frontier. 1st ed., O’Reilly Media, 24 Sept. 2024.
Holley, Kerrie, and Siupo Becker M.D. AI-First Healthcare: AI Applications in the Business and Clinical Management of Health. 1st ed., O’Reilly Media, 25 May 2021.
