Dangers of AI – Bias and Discrimination
Why it matters: AI bias and discrimination can perpetuate societal inequalities, requiring ethical and technical solutions for fair outcomes.
Everything AI, Robotics, and IoT
Sanksshep Mahendra is a technology executive with success in driving, vision, strategy, design, and execution of software engineering for the web, mobile, apps, social, voice, IoT, applications along with Machine learning and AI. His expertise lies in partnering with business leaders, powering through roadblocks, and leading global teams to deliver disruptive products that advance the organization’s mission and capture game-changing results in the market. Sanksshep Mahendra has a lot of experience in M&A and compliance, he holds a Master's degree from Pratt Institute and executive education from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, in AI, Robotics, and Automation.
Why it matters: AI bias and discrimination can perpetuate societal inequalities, requiring ethical and technical solutions for fair outcomes.
Why it matters: Explainable AI aims to make machine learning models transparent, enhancing user trust and facilitating ethical, accountable decisions.
Why it matters: AI transparency is crucial for ethical use, building public trust, and enabling accountability in algorithmic decision-making.
Why it matters: The Turing Test evaluates a machine’s ability to exhibit human-like intelligence through natural language conversation.
Why it matters: Chandrayaan-3 achieved a historic soft landing on the Moon’s South Pole, showcasing India’s advanced space capabilities.
Why it matters: The dangers of AI to humankind encompass ethical dilemmas, privacy erosion, and increased societal inequality.
Why it matters: Generative AI is transforming industries by automating creative tasks, yet it poses ethical and governance challenges.
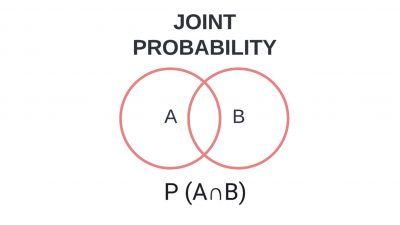
Why it matters: Joint probability measures the likelihood of multiple events happening at the same time. Let us learn more about it.
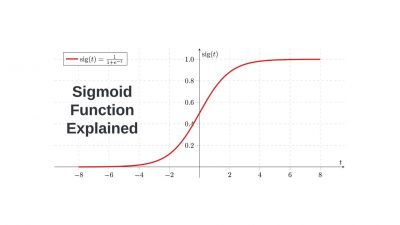
Why it matters: The Sigmoid function is a commonly used activation function in neural networks, especially for binary classification problems.
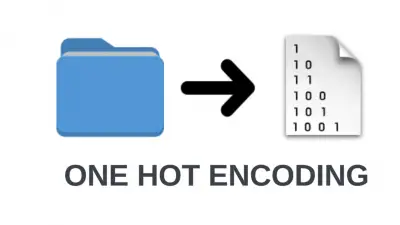
Why it matters: One-Hot Encoding transforms categorical variables into a binary numerical format, making them machine-friendly.